前言 最近做回后台开发,重新抓起以前学过的SSM(Spring+Spring MVC+Mybatis),但是发现配置实在过于复杂,好多东西配置起来麻烦,虽然最终是配置出来了,但是还是感觉开发速度跟不上,本来打算切换到jfianl,但是后来发现需要用的几个框架不支持jfianl,如Swagger2(根据代码中的注解生成接口文档和测试页面,非常的方便);同时我也不愿意放弃SpringMVC强大的验证参数模块,jfianl中好像只能手动验证(当然我对jfianl只处于简单的开发,并不是特别熟),而SpringMVC中,直接就能通过注解来确定哪些参数是必须的,哪些不是必须的,这对于写接口的人来说,方便了很多,所以决定还是使用Spring家族的东西,下面先一一介绍下本文的主角们
spring-boot是由Pivotal 团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。通过这种方式,Boot致力于在蓬勃发展的快速应用开发领域(rapid application development)成为领导者
多年以来,Spring IO 平台饱受非议的一点就是大量的XML配置以及复杂的依赖管理。在2013年的SpringOne 2GX 会议上,Pivotal的CTO Adrian Colyer回应了这些批评,并且特别提到该平台将来的目标之一就是实现免XML配置的开发体验。Boot所实现的功能超出了这个任务的描述,开发人员不仅不再需要编写XML,而且在一些场景中甚至不需要编写繁琐的import语句。在对外公开的beta版本刚刚发布之时,Boot描述了如何使用该框架在140个字符内实现可运行的web应用,从而获得了极大的关注度,该样例发表在tweet 上
当然上面又是我抄过来的,因为我觉得要我去介绍一个框架是什么的时候,我只会说我的理解,但是我的理解不能让大家知道它的背景,所以抄了上面那段,那么下面就是我理解的Spring boot是个什么东西
无需繁琐配置的Spring集合包 Spring boot本身并不是什么新的框架,它可以说只是Spring大家族的一个集合包,当然这个集合包吧基础的配置都给我配置好了,我们无需再进行繁琐的xml配置,甚至是都不用配置web.xml,因为spring boot内部自己集成了一个tomcat,直接通过run的方式就能启动,打包也一样,都可以不用部署tomcat了,当然是针对小项目,大项目肯定是要对中间件进行一些优化的
MyBatis是一个支持普通SQL查询,存储过程和高级映射的优秀持久层框架。MyBatis消除了几乎所有的JDBC代码和参数的手工设置以及对结果集的检索封装。MyBatis可以使用简单的XML或注解用于配置和原始映射,将接口和Java的POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录。当然我个人更倾向用注解,因为实在是不怎么喜欢配置xml,尤其是eclipse经常因为xml的一些问题卡主,导致编译要等xml验证通过后才能编译,而我用Mybatis最主要的地方就是因为不用像JDBC那样自己一个属性一个属性来赋值
Druid是一个JDBC组件,它包括三部分:
DruidDriver 代理Driver,能够提供基于Filter-Chain模式的插件体系。
可以监控数据库访问性能,Druid内置提供了一个功能强大的StatFilter插件,能够详细统计SQL的执行性能,这对于线上分析数据库访问性能有帮助。
替换DBCP和C3P0。Druid提供了一个高效、功能强大、可扩展性好的数据库连接池。
数据库密码加密。直接把数据库密码写在配置文件中,这是不好的行为,容易导致安全问题。DruidDruiver和DruidDataSource都支持PasswordCallback。
SQL执行日志,Druid提供了不同的LogFilter,能够支持Common-Logging、Log4j和JdkLog,你可以按需要选择相应的LogFilter,监控你应用的数据库访问情况。
扩展JDBC,如果你要对JDBC层有编程的需求,可以通过Druid提供的Filter-Chain机制,很方便编写JDBC层的扩展插件。
其实说简单点Druid就是一个功能强大,性能优秀的数据库连接池 ,是由阿里巴巴的大牛们开发的,除了性能好之外,我最喜欢的就是它的监控功能了,连github上的说明都是“为监控而生的数据库连接池!”
关于Swagger的介绍和非代码搭建 ,在之前的文章已经说过了,不过这里的Swagger2只是版本号为2而已,很多核心的东西都没怎么变化,当然如果不用和代码封装在一起,也可以参考Swagger的介绍和非代码搭建 ,不过本文主要讲述在代码中集成,所以不再过多描述
mybatis-generator是用来根据数据自动生成实体bean和一些常规查询语句的插件,有了这个就不用再一个一个实体bean来写了,而且普通的查询也可以使用自动生成sql语句查询出来
开始搭建 一、创建项目 首先创建一个maven项目,当然最好创建maven-archetype-webapp,原因无他,主要是因为很多时候我还是需要把项目部署到优化过配置的tomcat获取其他容器中,当然也可以创建普通的maven项目
二、添加依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-devtools</artifactId > <optional > true</optional > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > io.springfox</groupId > <artifactId > springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId > <version > 2.2.2</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > io.springfox</groupId > <artifactId > springfox-swagger2</artifactId > <version > 2.2.2</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 1.1.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba</groupId > <artifactId > druid</artifactId > <version > 1.0.26</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 5.0.5</version > </dependency >
其中spring-boot-devtools不是必须,只是如果你想在运行的时候,修改了代码能自动更新,而不用手动重启,就需要加上
三、添加Applcation类 这个就是程序的入口类了,代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 package wang.raye.springboot;import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan;import org.springframework.boot.web.support.SpringBootServletInitializer;@MapperScan("wang.raye.springboot.model.mapper") @SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer { public static void main (String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class); } }
想要运行项目时可以直接运行此类就可以,如你所见,其中有main方法,所以可以直接运行
下面说说3个注解的含义
**@MapperScan(“wang.raye.springboot.model.mapper”)**,扫描wang.raye.springboot.model.mapper下面的mapper接口,其中mapper下面的接口是由mybatis-generator自动生成的,会在后面细说,现在就先知道是个什么东西就行了@SpringBootApplication 很多Spring Boot开发者总是使用 @Configuration , @EnableAutoConfiguration 和 @ComponentScan 注解他们的main类。由于这些注解被如此频繁地一块使用(特别是你遵循以上最佳实践时),Spring Boot提供一个方便的 @SpringBootApplication 选择。该 @SpringBootApplication 注解等价于以默认属性使用 @Configuration , @EnableAutoConfiguration 和 @ComponentScan
@ServletComponentScan 有此注解后,项目中如果需要使用java原生的servlet和filter,可以在类中使用注解实现,主要是配置Druid监控时需要用到
四、创建配置文件 虽然spring boot可以不用配置xml,但是也并不是完全不需要配置文件,当然不用配置文件也能跑起来,只是有配置文件我们可以配置很多东西,只是不用像以前xml那么麻烦,首先需要在resource文件夹下面创建application.yml文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 server: port: 80 spring: application: name: admin-managee datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.157.133:3306/springboot username: raye password: 123456 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource druid: max-active: 20 initial-size: 1 min-idle: 3 max-wait: 60000 time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000 min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000 test-while-idle: true test-on-borrow: false test-on-return: false debug: true
相信这个文件很容易看懂,首先server:下面的port:80这个是定义了运行的端口,之前说过spring boot内置了tomcat服务器,所以如果要使用内置的tomcat并且不想用8080端口,就需要在这里配置
下面就是datasource的配置,这样不写进代码有个好处,那就是如果是给客户用的程序,可以很方便的修改数据库配置,而不用重新编译,当然如果你是打包jar我估计是要重新编译的,如果是war,那么就可以解压出来直接修改application.yml而不用重新编译了
而debug:true就是说明当时是调试状态,这样就会输出很多log
五、创建Druid数据源配置类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 package wang.raye.springboot.config;import java.sql.SQLException;import javax.sql.DataSource;import org.springframework.boot.bind.RelaxedPropertyResolver;import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;@Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement public class DruidDataSourceConfig implements EnvironmentAware { private RelaxedPropertyResolver propertyResolver; public void setEnvironment (Environment env) { this .propertyResolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver (env, "spring.datasource." ); } @Bean public DataSource dataSource () { System.out.println("注入druid!!!" ); DruidDataSource datasource = new DruidDataSource (); datasource.setUrl(propertyResolver.getProperty("url" )); datasource.setDriverClassName(propertyResolver.getProperty("driver-class-name" )); datasource.setUsername(propertyResolver.getProperty("username" )); datasource.setPassword(propertyResolver.getProperty("password" )); datasource.setInitialSize(Integer.valueOf(propertyResolver.getProperty("initial-size" ))); datasource.setMinIdle(Integer.valueOf(propertyResolver.getProperty("min-idle" ))); datasource.setMaxWait(Long.valueOf(propertyResolver.getProperty("max-wait" ))); datasource.setMaxActive(Integer.valueOf(propertyResolver.getProperty("max-active" ))); datasource.setMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(Long.valueOf(propertyResolver.getProperty("min-evictable-idle-time-millis" ))); try { datasource.setFilters("stat,wall" ); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return datasource; } }
主要是创建一个druid的DruidDataSource 返回并告诉spring boot这是一个bean
六、创建Druid的监控servlet和filter 创建监控Servlet
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package wang.raye.springboot.config;import javax.servlet.annotation.WebInitParam;import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet;@SuppressWarnings("serial") @WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/druid/*", initParams={ @WebInitParam(name="allow",value="127.0.0.1,192.168.1.126"),// IP白名单 (没有配置或者为空,则允许所有访问) @WebInitParam(name="deny",value="192.168.1.111"),// IP黑名单 (存在共同时,deny优先于allow) @WebInitParam(name="loginUsername",value="Raye"),// 用户名 @WebInitParam(name="loginPassword",value="123456"),// 密码 @WebInitParam(name="resetEnable",value="false")// 禁用HTML页面上的“Reset All”功能 }) public class DruidStatViewServlet extends StatViewServlet {}
@WebServlet 表明这是一个Servlet,和之前Application中的@ServletComponentScan相对应使用创建filter
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 package wang.raye.springboot.config;import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;import javax.servlet.annotation.WebInitParam;import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.WebStatFilter;@WebFilter(filterName="druidWebStatFilter",urlPatterns="/*", initParams={ @WebInitParam(name="exclusions",value="*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.bmp,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*")// 忽略资源 }) public class DruidStatFilter extends WebStatFilter {}
同样**@WebFilter**表明此类是一个拦截器
创建好之后,我们访问http://localhost/druid/index.html,会自动跳到http://localhost/druid/login.html登录页面,登录进去会出现以下界面
七、配置mybatis 其实mybatis之前就已经配置好了,就是Application 类的**@MapperScan(“wang.raye.springboot.model.mapper”)**注解,这个注解说明了要扫描的mybatis的mapper接口包,当然如果是用xml的话应该还需要其他配置,不过我个人并不喜欢用xml的方式,所以也没有怎么研究
八、配置mybatis-generator 配置MyBatis-generator自动生成实体bean,首先需要在pom.xml中添加相关插件依赖,注:我是用插件的方式来生成实体bean的,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 <build > <finalName > springboot</finalName > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.mybatis.generator</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-generator-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 1.3.5</version > <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 5.0.5</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-spring</artifactId > <version > 1.2.2</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis</artifactId > <version > 3.2.4</version > </dependency > </dependencies > <executions > <execution > <id > Generate MyBatis Artifacts</id > <phase > package</phase > <goals > <goal > generate</goal > </goals > </execution > </executions > <configuration > <verbose > true</verbose > <overwrite > true</overwrite > <configurationFile > src/main/resources/mybatis-generator.xml</configurationFile > </configuration > </plugin > <plugin > <artifactId > maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId > <configuration > <encoding > UTF-8</encoding > <source > 1.5</source > <target > 1.5</target > </configuration > </plugin > </plugins > </build >
其中除了springboot是pom.xml默认的节点外,其他都是配置Mybatis-generator的,当然还有顶部的
1 2 3 4 5 <properties > <project.build.sourceEncoding > UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding > <entity.target.dir > src/main/java/</entity.target.dir > <dao.resources.dir > src/main/resources/</dao.resources.dir > </properties >
这个是用来在mybatis-generator.xml 中需要使用的
下面开始配置mybatis-generator.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd" > <generatorConfiguration > <context id ="DB2Tables" targetRuntime ="MyBatis3" defaultModelType ="flat" > <plugin type ="org.mybatis.generator.plugins.RenameExampleClassPlugin" > <property name ="searchString" value ="[e|E]xample$" /> <property name ="replaceString" value ="Criteria" /> </plugin > <commentGenerator > <property name ="suppressDate" value ="true" /> </commentGenerator > <jdbcConnection driverClass ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" connectionURL ="jdbc:mysql://192.168.157.133:3306/springboot" userId ="root" password ="1993316" > </jdbcConnection > <javaTypeResolver > <property name ="forceBigDecimals" value ="false" /> </javaTypeResolver > <javaModelGenerator targetPackage ="wang.raye.springboot.model" targetProject ="${entity.target.dir}" > <property name ="enableSubPackages" value ="true" /> <property name ="trimStrings" value ="true" /> </javaModelGenerator > <sqlMapGenerator targetPackage ="wang.raye.springboot.model.mapper" targetProject ="${dao.resources.dir}" > <property name ="enableSubPackages" value ="true" /> </sqlMapGenerator > <javaClientGenerator type ="ANNOTATEDMAPPER" targetPackage ="wang.raye.springboot.model.mapper" implementationPackage ="wang.raye.springboot.model.mapper.impl" targetProject ="${entity.target.dir}" > <property name ="enableSubPackages" value ="true" /> </javaClientGenerator > <table tableName ="user" domainObjectName ="User" > </table > </context > </generatorConfiguration >
其实需要自己修改数据库配置,因为插件不会读取spring boot中的数据库配置,所以需要在mybatis-generator.xml中配置好数据库,同时也需要修改自己的包名
table 节点中的tableName是指在数据库中的表名,domainObjectName是只生成的实体bean的类名,当然domainObjectName可以不用配置,会默认生成,当然如果有特殊需要可以配置
配置Swagger2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 package wang.raye.springboot;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;import wang.raye.springboot.model.User;@Configuration @EnableSwagger2 public class SwaggerConfig { @Bean public Docket testApi () { return new Docket (DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("wang.raye.springboot" )) .paths(PathSelectors.any()).build(); } private ApiInfo apiInfo () { ApiInfo apiInfo = new ApiInfo ("SpringBoot学习demo" , "Spring boot + swagger + mybatis + druid" , "1.0" , "NO terms of service" , "admin@raye.wang" , "RayeBlog" , "http://www.raye.wang/" ); return apiInfo; } }
相信看代码很容易看懂,我就不多说了
编写demo 至此,环境配置都配置好了,然后我创建一个简单的接口来添加用户,首先看看我的表结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user `;CREATE TABLE `user ` ( `id` int (11 ) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` varchar (30 ) NOT NULL , `psw` varchar (40 ) NOT NULL , PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE= InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT= 0 DEFAULT CHARSET= utf8;
因为只是做演示,所以非常简单,然后看我生成的User.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 package wang.raye.springboot.model;public class User { private Integer id; private String username; private String psw; public Integer getId () { return id; } public void setId (Integer id) { this .id = id; } public String getUsername () { return username; } public void setUsername (String username) { this .username = username == null ? null : username.trim(); } public String getPsw () { return psw; } public void setPsw (String psw) { this .psw = psw == null ? null : psw.trim(); } }
当然我是删除了很多自动生成的注释,因为看着太烦,不适合在博客上展示,然后看看UserMapper.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 package wang.raye.springboot.model.mapper;import java.util.List;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.DeleteProvider;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.InsertProvider;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Result;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Results;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.SelectProvider;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.UpdateProvider;import org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType;import wang.raye.springboot.model.User;import wang.raye.springboot.model.UserCriteria;public interface UserMapper { @SelectProvider(type=UserSqlProvider.class, method="countByExample") long countByExample (UserCriteria example) ; @DeleteProvider(type=UserSqlProvider.class, method="deleteByExample") int deleteByExample (UserCriteria example) ; @Delete({ "delete from user", "where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}" }) int deleteByPrimaryKey (Integer id) ; @Insert({ "insert into user (id, username, ", "psw)", "values (#{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}, #{username,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, ", "#{psw,jdbcType=VARCHAR})" }) int insert (User record) ; @InsertProvider(type=UserSqlProvider.class, method="insertSelective") int insertSelective (User record) ; @SelectProvider(type=UserSqlProvider.class, method="selectByExample") @Results({ @Result(column="id", property="id", jdbcType=JdbcType.INTEGER, id=true), @Result(column="username", property="username", jdbcType=JdbcType.VARCHAR), @Result(column="psw", property="psw", jdbcType=JdbcType.VARCHAR) }) List<User> selectByExample (UserCriteria example) ; @Select({ "select", "id, username, psw", "from user", "where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}" }) @Results({ @Result(column="id", property="id", jdbcType=JdbcType.INTEGER, id=true), @Result(column="username", property="username", jdbcType=JdbcType.VARCHAR), @Result(column="psw", property="psw", jdbcType=JdbcType.VARCHAR) }) User selectByPrimaryKey (Integer id) ; @UpdateProvider(type=UserSqlProvider.class, method="updateByExampleSelective") int updateByExampleSelective (@Param("record") User record, @Param("example") UserCriteria example) ; @UpdateProvider(type=UserSqlProvider.class, method="updateByExample") int updateByExample (@Param("record") User record, @Param("example") UserCriteria example) ; @UpdateProvider(type=UserSqlProvider.class, method="updateByPrimaryKeySelective") int updateByPrimaryKeySelective (User record) ; @Update({ "update user", "set username = #{username,jdbcType=VARCHAR},", "psw = #{psw,jdbcType=VARCHAR}", "where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}" }) int updateByPrimaryKey (User record) ; }
同样删除了注释,当然还会自动生成UserCriteria.java 和UserSqlProvider,这2个类主要用于模板查询,用过myBatis应该都知道,就不贴出来了,主要是我们的demo中也不会用到
一、创建UserServer接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package wang.raye.springboot.server;import java.util.List;import wang.raye.springboot.model.User;public interface UserServer { public boolean add (User user) ; }
二、创建UserServerImpl
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 package wang.raye.springboot.server.impl;import java.util.List;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;import wang.raye.springboot.model.User;import wang.raye.springboot.model.mapper.UserMapper;import wang.raye.springboot.server.UserServer;@Repository public class UserServerImpl implements UserServer { @Autowired private UserMapper mapper; public boolean add (User user) { return mapper.insert(user) > 0 ; } public List<User> findAll () { return mapper.selectByExample(null ); } }
三、创建UserController
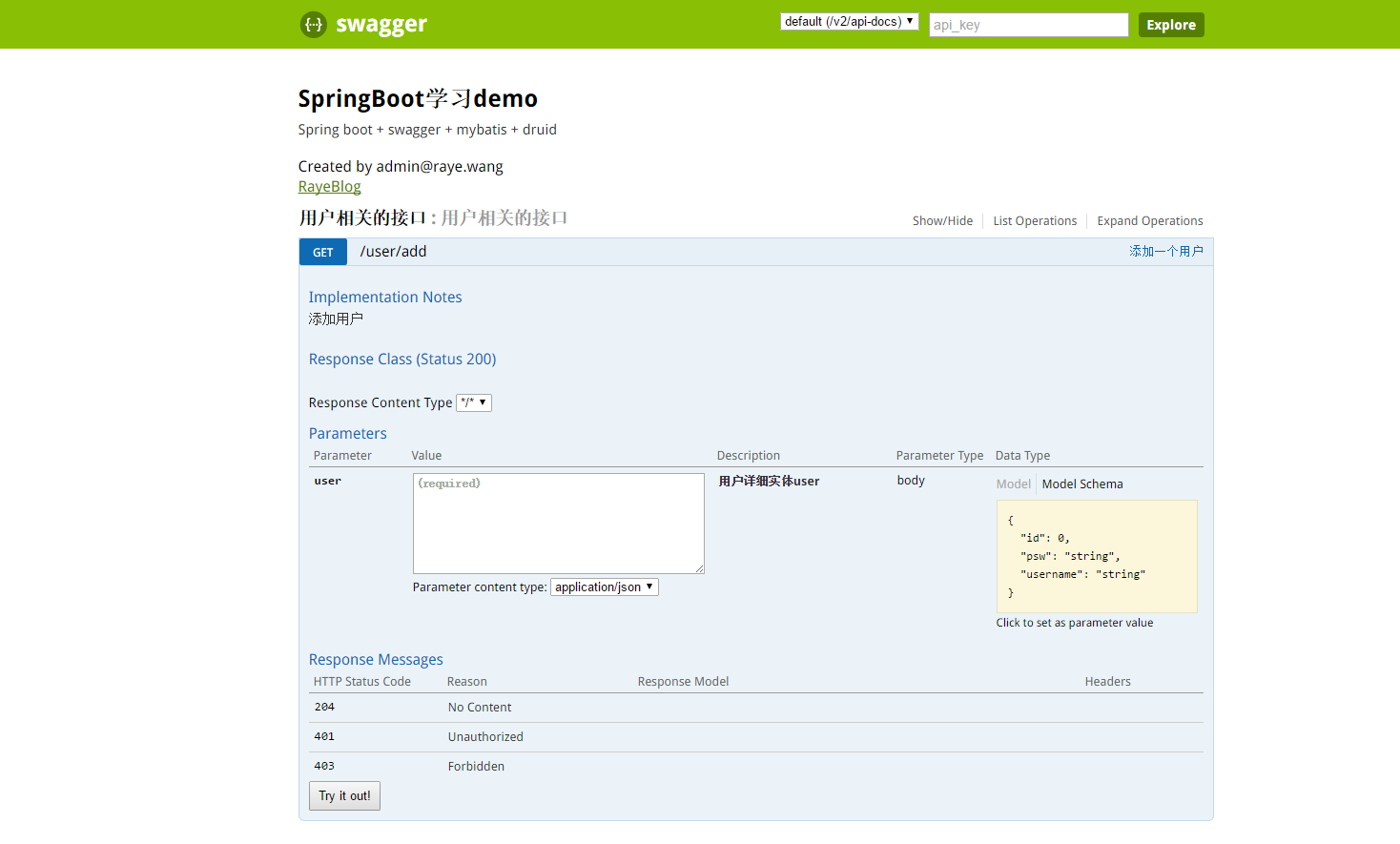
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package wang.raye.springboot.controller;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import io.swagger.annotations.Api;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;import wang.raye.springboot.model.User;import wang.raye.springboot.server.UserServer;@Api(value="用户相关的接口") @RestController @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController { @Autowired private UserServer server; @RequestMapping("/add") @ApiOperation(notes="添加用户",value="添加一个用户",httpMethod="POST") @ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细实体user", required = true, dataType = "User") public String add (@RequestBody User user) { return "hello " +server.add(user); } }
到此一个接口就完成了,我们可以到swagger2的文件页面去测试http://localhost/swagger-ui.htm 注意如果端口不是80需要加上端口号,点开页面中的用户相关的接口 和GET /user/add可以看到如下页面
我们可以在parameters处输入
1 2 3 4 { "psw" : "Raye" , "username" : "123456" }
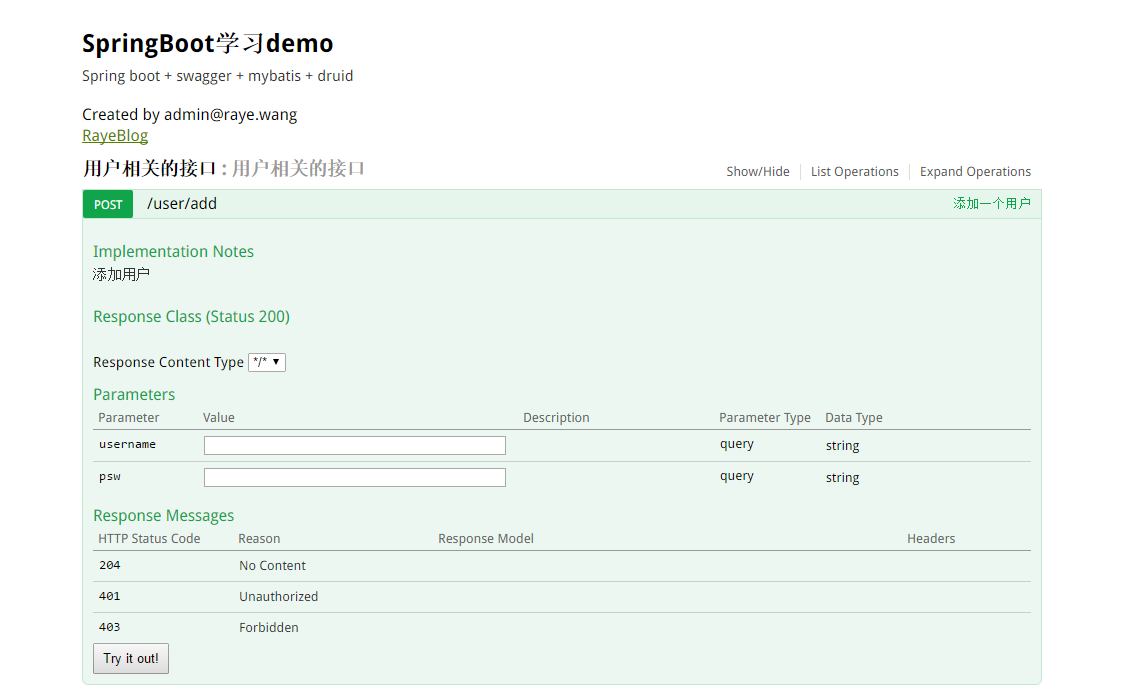
点击try it out就可以测试了,当然你也可能不想用json的方式,可以使用
1 2 3 4 @ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(name="username",paramType="query",dataType="string"), @ApiImplicitParam(name="psw",paramType="query",dataType="string") })
代替
1 @ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细实体user", required = true, dataType = "User")
同时为了隐藏user参数,需要在SwaggerConfig类的testApi方法中添加.ignoredParameterTypes(User.class)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Bean public Docket testApi () { return new Docket (DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .ignoredParameterTypes(User.class) .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("wang.raye.springboot" )) .paths(PathSelectors.any()).build(); }
测试界面就会变为
结尾 好了,到这里一个Springboot+Mybatis+Druid+Swagger2+mybatis-generator框架环境就搭建完成了,欢迎大家留言交流,另外附上本项目
demo oschina地址
demo github地址